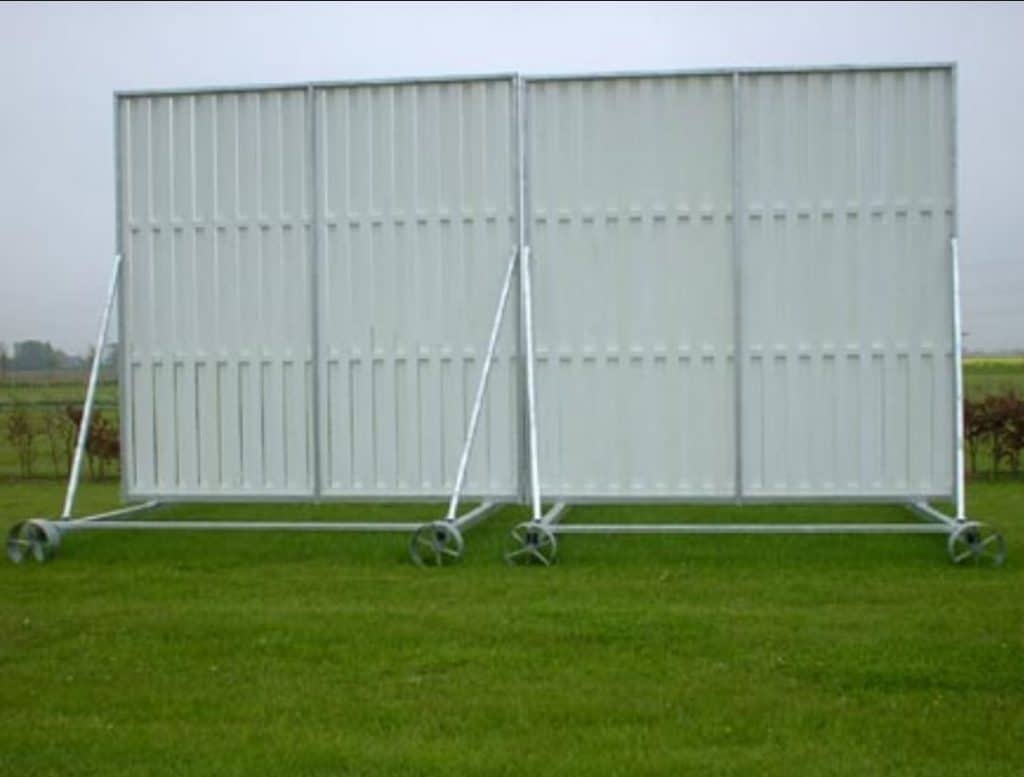
A sight screen is a large board made of wood or polycarbonate material or a large clothing sheet that is positioned in two specific areas on the cricket ground. These specific positions are areas outside the boundary line. One sight screen is placed behind the bowler and one is placed behind the wicketkeeper.
But why are they really placed in those areas? The onus is on the batsman. When a bowler bowls, it is very important for the batsman to focus on the bowler’s hand right from the time he releases the ball till the time the bat contacts it. Any movement or even a hint of disturbance from the bowler’s background is a mode of distraction for the batsman. Hence, the sightscreen serves as a static background for the batsman to completely focus on the bowler.

Sightscreens can be of two colors – Black or White. The black colored sightscreen is used in ODIs and T20s where the white hue of the ball is in contrast with the sightscreen and hence better visibility. White sightscreens are used in test matches where the red and pink colored balls can be seen with ease.
Sightscreens can be moved as there are wheels attached to them. One might often notice the batsman signalling the man controlling the sightscreen position to move it in the desired direction based on the batsman’s comfort.
It is interesting to note that considering how sensitive the sightscreen is for the batsman, it is within the laws of the game to place a fielder behind the umpire. Though not considered in the spirit of the game, such a tactic has been employed by many teams in the past. However, if a fielder is placed there, it is important for him to not move an inch till the ball has reached the batsman else the bowling side will be penalized.
In modern times sight screens also serve as a mode of advertising. Various sponsors display their digital ads in between the overs on sightscreens. Thus, sightscreens are mandatory for cricket both in terms of sporting ease and commercial gains.